Accounting Equation Definition, Formula, Example
发布时间:2023-06-21来源:家德乐淋浴房

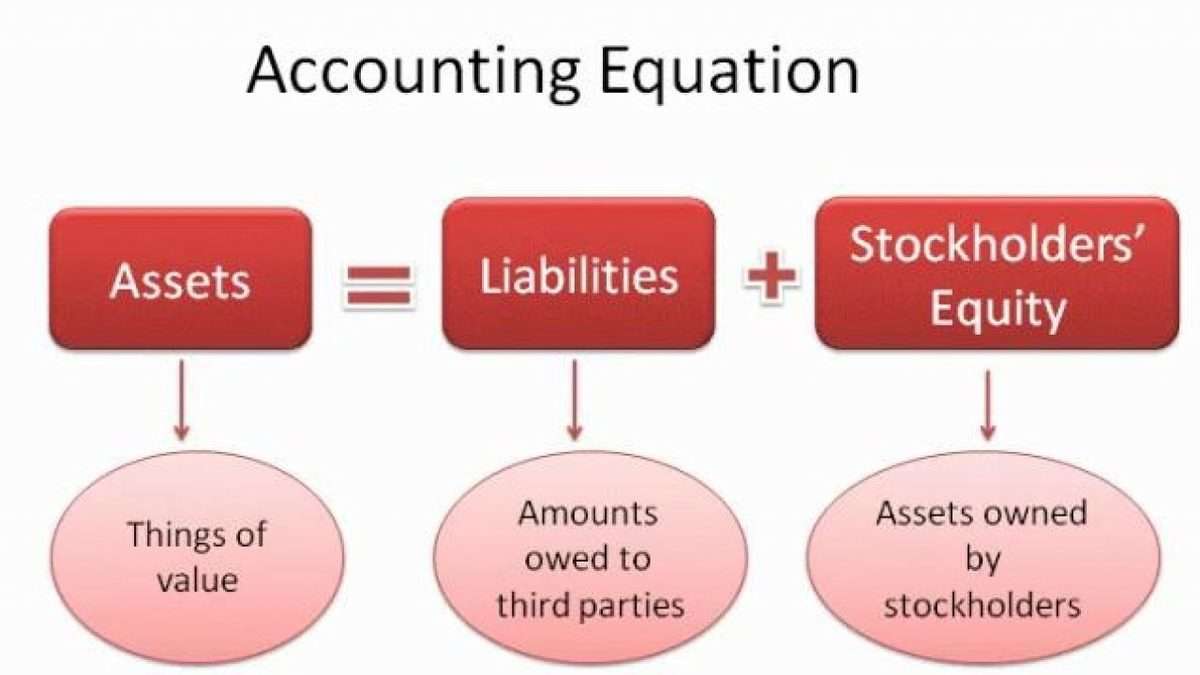
You can find a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity on key financial statements, such as balance sheets and income statements (also called profit and loss statements). These financial documents give overviews of the company’s financial position at a given point in time. The accounting equation ensures the balance sheet is balanced, which means the company is recording transactions accurately. Accounting equation describes that the total value of assets of a business entity is always equal to its liabilities plus owner’s equity.
Purchase of Equipment in Cash
The capital would ultimately belong to you as the business owner. In the case of a limited liability company, capital would be referred to as ‘Equity’. If a transaction is completely omitted from the accounting books, it will not unbalance the accounting equation.
Assets, Liabilities, And Equity
The Accounting Equation is the primary accounting principle stating that a business's total assets are equivalent to the sum of its liabilities & owner's capital. It is also known as the Balance Sheet Equation & it forms the basis of the double-entry accounting system. At the same time, it incurred in an obligation to pay the bank. This increases the accounts receivable (Asset) account by $55,000, and increases the revenue (Equity) account.
- Creditors have preferential rights over the assets of the business, and so it is appropriate to place liabilities before the capital or owner's equity in the equation.
- Of course, this lead to the chance of human error, which is detrimental to a company’s health, balance sheets, and investor ability.
- Shareholders’ equity is the total value of the company expressed in dollars.
- The global adherence to the double-entry accounting system makes the account-keeping and -tallying processes more standardized and foolproof.
- So, as long as you account for everything correctly, the accounting equation will always balance no matter how many transactions are involved.
Shareholders’ Equity in the Accounting Equation
The assets have been decreased by $696 but liabilities have decreased by $969 which must have caused the accounting equation to go out of balance. If an accounting equation does not balance, it means that the accounting transactions are not properly recorded. To calculate the accounting equation, we first need to work out the amounts of each asset, liability, and equity in Laura’s business. Like any brand new business, it has no assets, liabilities, or equity at the start, which means that its accounting equation will have zero on both sides. Ted is an entrepreneur who wants to start a company selling speakers for car stereo systems. After saving up money for a year, Ted decides it is time to officially start his business.
In short, the accounting equation does not ensure that reported financial information is correct - only that it follows certain rules regarding how information is to be recorded within an accounting system. The reason why the accounting equation is so important is that it is always true - and it forms the basis for all accounting transactions in a double entry system. At a general level, this means that whenever there the accounting equation is defined as: is a recordable transaction, the choices for recording it all involve keeping the accounting equation in balance. The accounting equation concept is built into all accounting software packages, so that all transactions that do not meet the requirements of the equation are automatically rejected. The Shareholders' Equity part of the equation is more complex than simply being the amount paid to the company by investors.
Liabilities in the Accounting Equation
He forms Speakers, Inc. and contributes $100,000 to the company in exchange for all of its newly issued shares. This business transaction increases company cash and increases equity by the same amount. A liability, in its simplest terms, is an amount of money owed to another person or organization. Said a different way, liabilities are creditors’ claims on company assets because this is the amount of assets creditors would own if the company liquidated. Now that we have a basic understanding of the equation, let’s take a look at each accounting equation component starting with the assets.
Drawings are amounts taken out of the business by the business owner. An asset is a resource that is owned or controlled by the company to be used for future benefits. Some assets are tangible like cash while others are theoretical or intangible like goodwill or copyrights. Accounts receivable list the amounts of money owed to the company by its customers for the sale of its products. Assets include cash and cash equivalents or liquid assets, which may include Treasury bills and certificates of deposit (CDs).
Hence, the account from which the amount is withdrawn gets credited, and there needs to be an account debited for the asset purchased (the account related to the asset purchased gets debited). Let us understand the different components of the equation in detail which will facilitate in understanding the calculation done by companies. The equation is an important concept used to assess the financial condition of the company.
Each transaction must be recorded so that the equation is in balance once the processing has taken place. Thus from the above details we can understand how to do accounting equation. Equity on the other hand is the shareholders’ claims on the company assets. This is the amount of money shareholders have contributed to the company for an ownership stake.
Analyze a company's financial records as an analyst on a technology team in this free job simulation. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. He is the sole author of all the materials on AccountingCoach.com. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
Recording accounting transactions with the accounting equation means that you use debits and credits to record every transaction, which is known as double-entry bookkeeping. The Liabilities part of the equation is usually comprised of accounts payable that are owed to suppliers, a variety of accrued liabilities, such as sales taxes and income taxes, and debt payable to lenders. Accounts payable include all goods and services billed to the company by suppliers that have not yet been paid. Accrued liabilities are for goods and services that have been provided to the company, but for which no supplier invoice has yet been received. In other words, the total amount of all assets will always equal the sum of liabilities and shareholders’ equity. Essentially, the representation equates all uses of capital (assets) to all sources of capital, where debt capital leads to liabilities and equity capital leads to shareholders’ equity.
